Info:
Title: Relation – Shift - Code: J7S9W1Contest: Venice / 2011
By: J. Combes / G. Brulè / Atelier CMJN
Views: 4058 Likes: 0
Votes:
BJARKE INGELS7 NERI OXMAN7 ELENA MANFERDINI4 MARIA LUDOVICA TRAMONTIN6 BOSTJAN VUGA106.8
Relation – Shift
SUB-VENICE Evolve to thrive RELATION-SHIFT A new sea-island relationship The sea rise is the direct consequence of one of the most dramatic effects of human activities. According to an IPCC report, the sea level could rise between 6 and 10 meters by 2100. The rise of the sea level already made its first victims. The islands of Vanuatu in the Pacific are already on the verge of disappearing and many more are to come.
“Beauty is an ephemeral flower” says a Bible proverb. This proverb might reflect particularly well in the case of Venice. Already flooded several times a year by ordinary storm surges, the Venice area would be greatly endangered by even a very small, additional rise in sea level (Pizaroli, 1991). Although no one seems to agree on the exact figures, it seems that nature is willing to keep this beauty ephemeral by dragging it into oblivion like it already did for Atlantis…
Venice and water has always been a hate love relationship, a perpetual fight with no winners as for now. As Venice is tumbling on its foundations and losing the battle, it seems pointless to try to maintain the current equilibrium between Venice and water as such. Finding a new equilibrium with water is the fate of Venice, the only way for this city to survive. “Accept your fate or be destroyed by it” says the proverb. We take this at face value and propose to give the flower some space and to change the equilibrium, so that Venice can survive, live and thrive.
In order to become “serene” again, the city needs to accommodate a proper structure that will stop the fight and set a new equilibrium between water and the city, even with a considerably higher sea level. This new equilibrium requires a shift of relationship between the sea and the island, we need to move from the “island over the sea” to the “island under the sea” paradigm. An “osmotic ring” will be the key in reestablishing the equilibrium between the city and the sea.
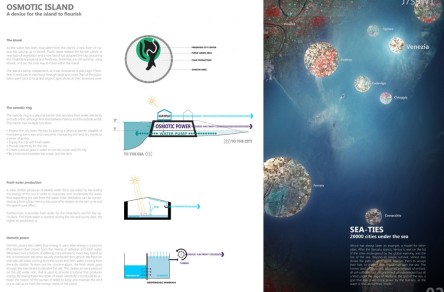
OSMOTIC ISLAND
A device for the island to thrive
The island
As the water has been evacuated from the island, a new form of nature has sprung up in Venice. Public areas replace the former canals. A new type of vegetation and a new fauna has adopted the city, procuring the inhabitants pleasure and freshness. Gondolas are still working, using wheels, and are the only way to travel within the island.
The island is being independent, as it was thousands of years ago. Therefore, it produces its own food, through lands and crops. Part of the population went back to local and organic agriculture, as their ancestors were.
The osmotic ring
The osmotic ring is a physical barrier that provides fresh water, electricity and sets a fine, although firm limit between Venice and the outside world. This barrier has multiple functions:
• Protect the city from the sea by placing a physical barrier capable of maintaining the ocean and constantly maintaining the land dry thanks to a series of pump
• Supply the city with fresh water
• Provide electricity for the city
• Create a leisure area in order to see the ocean and the city
• Be a transition between the ocean and the land
Fresh water production
A solar distiller produces drinkable water from sea water by harvesting the energy of the sun in order to evaporate and condensate the water, thus separating the salt from the water. Solar distillation can be considered as a form of bio-mimicry because of its relation to the rain cycle and the greenhouse effect.
Furthermore, it provides fresh water for the inhabitants and for the agriculture. The more water is needed, during the hot and sunny days, the higher its production is.
Osmotic power
Osmotic power, also called blue energy is used. Blue energy is a process that derives clean power from the mixing of saltwater and fresh water. Whenever two solutions of differing concentrations meet they blend so the concentration becomes equally distributed throughout. We have on one side salt water, coming from the ocean and fresh water, coming from the solar distiller. To even out the concentrations, the fresh water goes through the membrane to dissolve the salt. This creates an extra pressure on the salt water side, that is used to activate a turbine that produces energy. By mixing these two types of water, electricity is produced to activate the motors of the pumps in order to keep and maintain the land dry as well as to meet the energy needs of the island.
SEA-TIES
20000 cities under the sea
Venice has always been an example, a model for other cities. After the Vanuatu islands, Venice is next on the list of the cities endangered by the global warming and the rise of the sea. Beyond its simple survival, Venice also shows the path to other cities, teaches them to accept their fate, to change their equilibrium with the sea. The former land progressively becomes a network of entities, all self-sufficient but all connected, all independent but all united under the aegis of Neptune, the god of the sea, a god that was given more power by the humans, as the water is now above their heads.